Anal Carcinoma
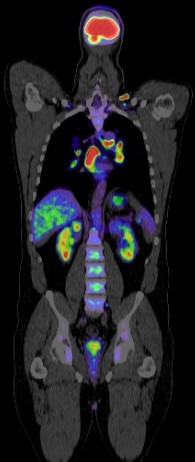

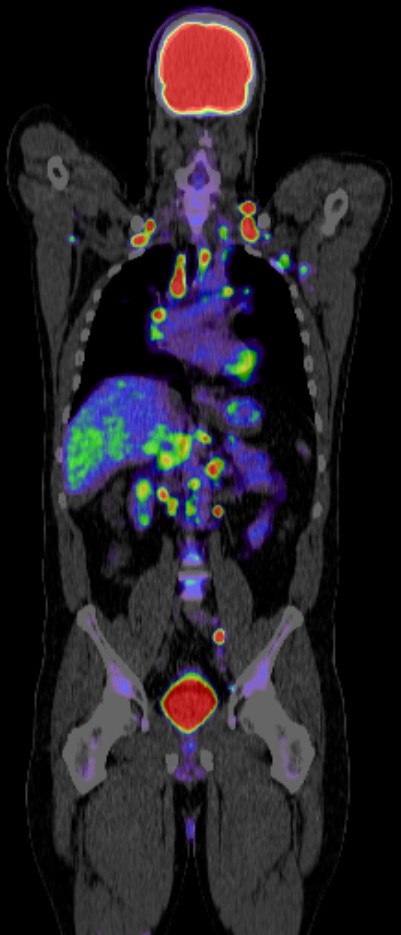
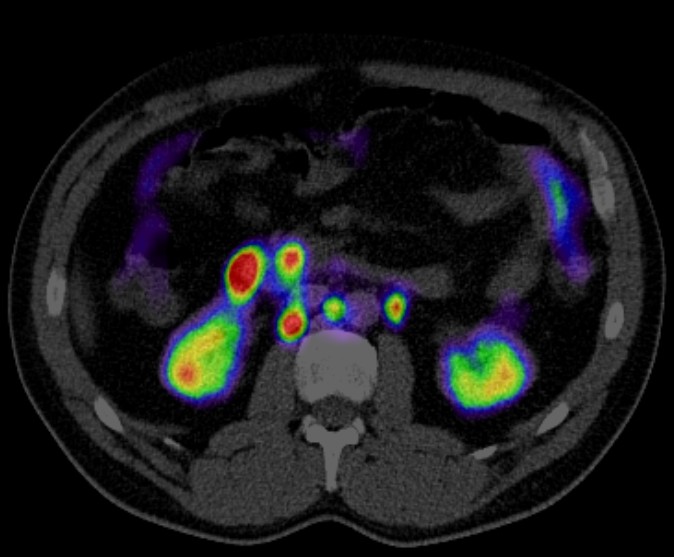
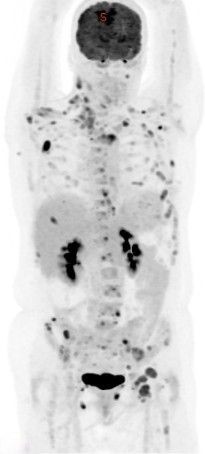
Positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET CT) has become a crucial imaging tool in the management of anal carcinoma due to its ability to combine metabolic and anatomic information. Here’s an overview of its role:
1. Diagnosis and Staging
- Initial Assessment: PET CT is used to detect primary anal tumors and to assess the extent of disease. It is especially useful for identifying metastatic lymph nodes that may not be detected by conventional imaging techniques like CT or MRI.
- Staging: Accurate staging is essential for determining the appropriate treatment plan. PET CT helps in staging by identifying the spread of cancer to lymph nodes and distant organs, such as the liver and lungs.
2. Treatment Planning
- Radiotherapy Planning: PET CT assists in delineating tumor boundaries more precisely, which is critical for planning radiotherapy. This ensures that the radiation dose is targeted effectively at the tumor while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues.
- Surgical Planning: For cases requiring surgical intervention, PET CT helps in defining the extent of the tumor and planning the surgical approach.
3. Monitoring Treatment Response
- Assessing Treatment Efficacy: PET CT is used to evaluate the response to chemoradiotherapy by comparing pre-treatment and post-treatment scans. It can distinguish between viable tumor tissue and post-treatment changes like fibrosis or necrosis.
- Early Detection of Recurrence: After treatment, PET CT can be used to monitor for signs of recurrence. It is more sensitive than other imaging modalities in detecting recurrent disease, allowing for earlier intervention.
4. Prognostic Value
- Predictive of Outcomes: The metabolic activity of the tumor, as measured by PET CT, can provide prognostic information. Higher uptake of the radioactive tracer often correlates with more aggressive disease and poorer outcomes.
5. Surveillance
- Follow-Up: Regular PET CT scans are sometimes performed during follow-up to ensure early detection of any recurrence. This is particularly useful in high-risk patients.
6. Research and Development
- Clinical Trials: PET CT is also used in clinical trials to evaluate new treatments and to understand the biology of anal carcinoma better. It provides a non-invasive way to monitor tumor behavior and response to novel therapies.
In summary, PET CT plays a significant role in the diagnosis, staging, treatment planning, monitoring, and follow-up of anal carcinoma. Its ability to provide detailed metabolic and anatomical information makes it a valuable tool in improving patient outcomes.
