Dementia
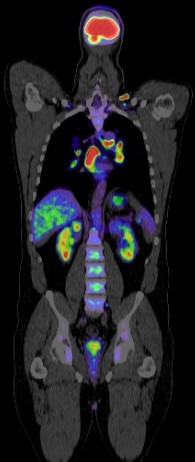

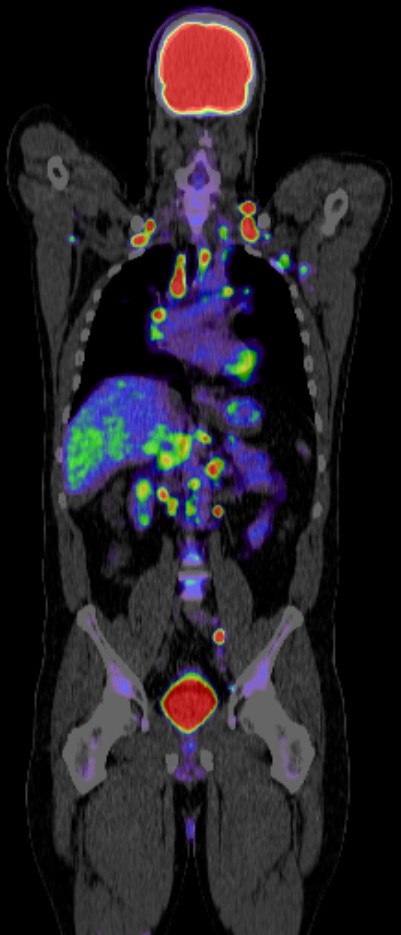
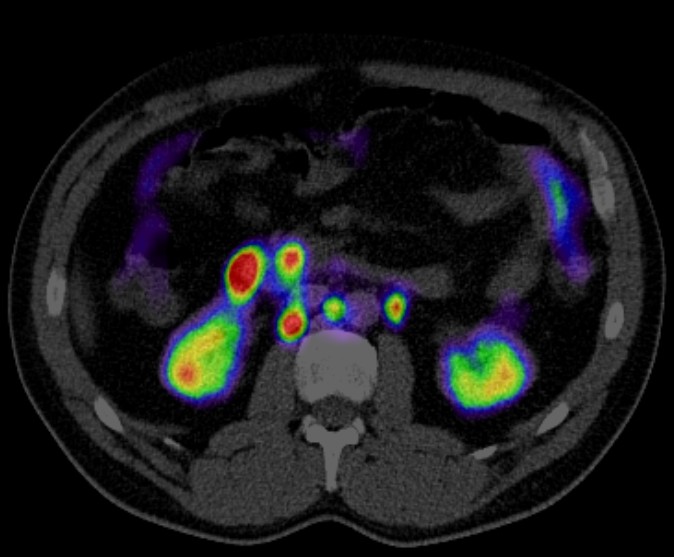
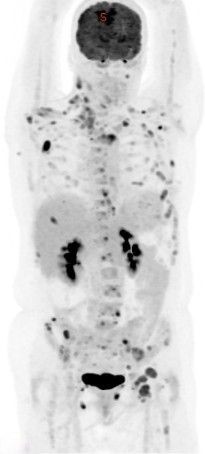
Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography (PET-CT) plays a significant role in the diagnosis, management, and research of dementia. Here are key points outlining its role:
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
- Early Detection: PET-CT can detect changes in brain metabolism and amyloid plaque deposition, which are early indicators of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and other forms of dementia before significant symptoms appear.
- Differential Diagnosis: Different types of dementia, such as Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal dementia, Lewy body dementia, and vascular dementia, show distinct patterns on PET-CT scans. This helps in differentiating among these conditions, which is crucial for appropriate treatment and management.
- Amyloid PET Imaging: This technique uses radiotracers that bind specifically to amyloid plaques. The presence of these plaques, which are characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease, can be confirmed, aiding in diagnosis.
Monitoring Disease Progression
- Tracking Metabolic Changes: PET-CT can monitor changes in glucose metabolism in the brain over time, providing insights into disease progression.
- Assessing Treatment Efficacy: By comparing PET-CT scans before and after treatment, clinicians can evaluate the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions.
Research and Understanding Pathophysiology
- Studying Disease Mechanisms: PET-CT helps researchers understand the underlying mechanisms of different types of dementia by visualizing changes in brain structure and function.
- Biomarker Development: The imaging data from PET-CT scans contribute to the development of biomarkers for early diagnosis and treatment response.
Personalized Medicine
- Tailoring Treatments: PET-CT aids in identifying specific types of dementia, enabling personalized treatment plans based on the unique characteristics of the patient’s condition.
- Predicting Outcomes: Imaging data can help predict disease progression and outcomes, guiding decision-making for both clinicians and patients.
Practical Applications in Clinical Settings
- Guiding Biopsy Decisions: In cases where a brain biopsy is considered, PET-CT can help in selecting the precise location for the procedure.
- Reducing Unnecessary Treatments: Accurate diagnosis via PET-CT can prevent misdiagnosis and the administration of ineffective treatments, improving patient care.
Challenges and Considerations
- Cost and Accessibility: PET-CT is an expensive imaging modality and may not be readily accessible in all healthcare settings.
- Radiation Exposure: The procedure involves exposure to radiation, which needs to be considered, especially in vulnerable populations.
PET-CT is a powerful tool in the realm of dementia, providing critical insights into diagnosis, progression, and treatment. Its ability to visualize biochemical changes in the brain non-invasively makes it invaluable in both clinical practice and research. However, considerations regarding cost, accessibility, and radiation exposure must be balanced against the benefits it provides.
