Head and Neck Cancer
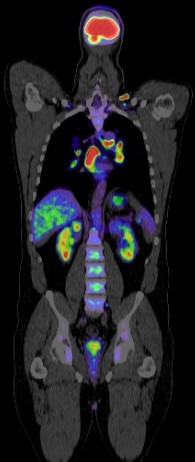

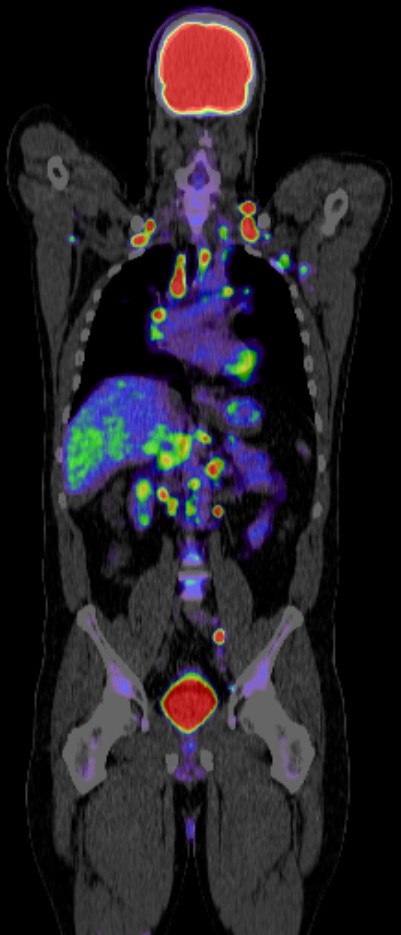
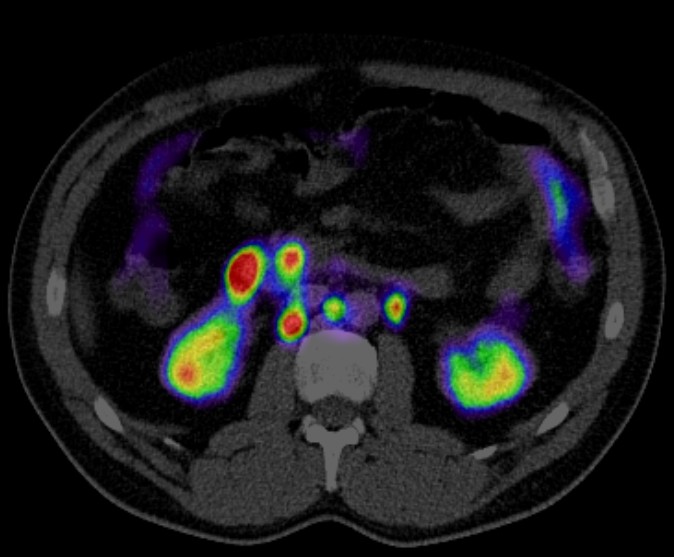
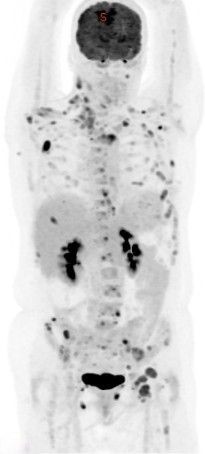
Positron Emission Tomography combined with Computed Tomography (PET CT) plays a significant role in the diagnosis, staging, treatment planning, and follow-up of head and neck cancers. Here’s an overview of its various roles:
1. Diagnosis
PET CT is valuable in detecting head and neck cancers, especially in cases where conventional imaging methods (CT or MRI) are inconclusive. The use of the radiotracer fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) helps identify metabolic activity associated with cancer cells.
2. Staging
Accurate staging is crucial for treatment planning. PET CT provides detailed information about the primary tumor, lymph node involvement, and distant metastasis, aiding in precise staging according to the TNM classification system.
3. Treatment Planning
- Radiotherapy: PET CT helps delineate the target areas for radiotherapy, ensuring the cancerous tissues are adequately covered while sparing healthy tissues.
- Surgery: It assists in planning surgical margins and identifying the extent of the tumor.
4. Response Assessment
After treatment, PET CT is used to assess the response to therapy. By comparing pre- and post-treatment scans, oncologists can evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment and detect residual disease.
5. Surveillance and Recurrence Detection
PET CT is effective in the early detection of recurrent disease, often before it becomes apparent on physical examination or other imaging modalities. It helps differentiate between scar tissue and active disease.
6. Guiding Biopsies
In cases where biopsy is needed, PET CT can guide the procedure by pinpointing the most metabolically active (and thus likely malignant) areas, increasing the diagnostic yield.
7. Identifying Unknown Primary Tumors
In patients presenting with metastatic neck lymph nodes and no obvious primary tumor, PET CT can help locate the primary tumor, which is often small and difficult to detect with other imaging techniques.
Advantages of PET CT in Head and Neck Cancer
- High Sensitivity and Specificity: PET CT provides high sensitivity and specificity for detecting head and neck cancers, especially for nodal involvement and distant metastasis.
- Functional Imaging: PET CT combines anatomical and functional imaging, offering a more comprehensive assessment compared to standalone imaging modalities.
- Early Detection: It allows for the early detection of recurrence, which can significantly impact patient outcomes.
Limitations
- False Positives/Negatives: Inflammatory and infectious processes can cause false positives, while small lesions may result in false negatives.
- Cost and Availability: PET CT is expensive and may not be available in all healthcare settings.
- Radiation Exposure: There is a concern about the radiation dose, although the benefits often outweigh the risks in cancer patients.
PET CT has become an integral part of the management of head and neck cancers, offering critical insights that aid in making informed decisions about patient care.
