Heart Conditions
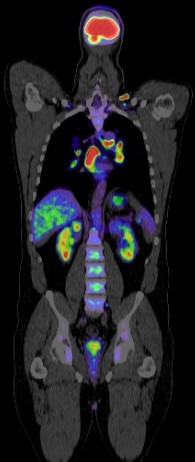

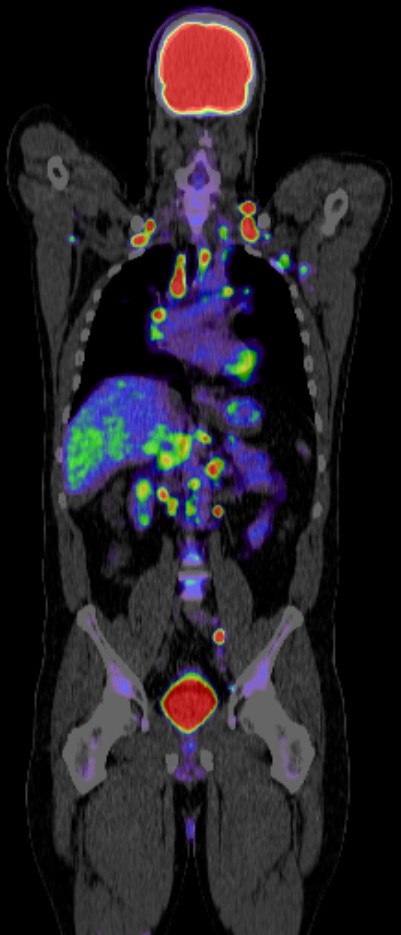
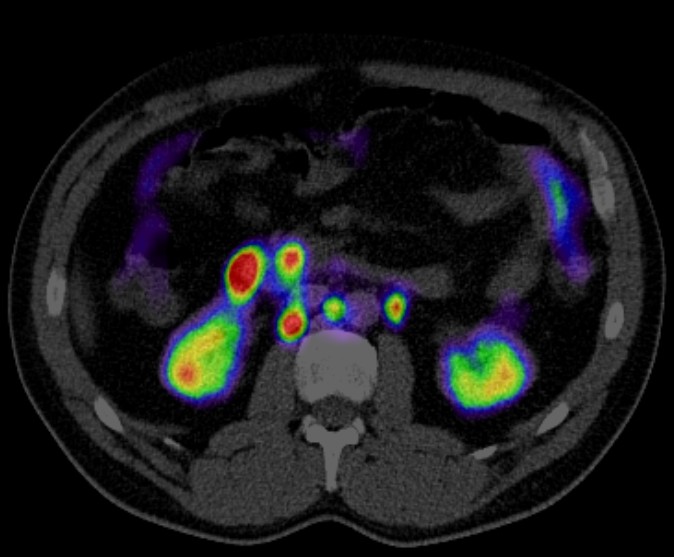
Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography (PET CT) is a powerful imaging tool in the diagnosis and management of heart disease. It combines the functional imaging capabilities of PET with the anatomical detail provided by CT, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of cardiovascular conditions. Here are some key roles of PET CT in heart disease:
1. Assessment of Myocardial Perfusion:
PET CT is highly effective in evaluating myocardial perfusion, particularly in detecting areas of reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. It helps in:
- Diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD).
- Determining the severity and extent of ischemia.
- Evaluating the efficacy of revascularization procedures.
2. Myocardial Viability:
PET CT can assess myocardial viability by differentiating between viable and non-viable heart tissue. This is crucial for:
- Planning revascularization strategies.
- Predicting recovery of function after revascularization in patients with left ventricular dysfunction.
3. Cardiac Sarcoidosis:
PET CT is valuable in diagnosing and managing cardiac sarcoidosis by:
- Detecting active inflammation.
- Monitoring response to treatment.
4. Cardiac Tumors:
PET CT helps in the detection and characterization of cardiac tumors, providing information about their metabolic activity and aiding in distinguishing benign from malignant lesions.
5. Infective Endocarditis:
In cases of suspected infective endocarditis, PET CT can detect inflammation and infection, helping to:
- Confirm diagnosis.
- Identify extracardiac sites of infection.
6. Vascular Inflammation:
PET CT is useful in assessing vascular inflammation and atherosclerotic plaque activity, which are important in:
- Identifying high-risk plaques that may lead to future cardiovascular events.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of anti-inflammatory therapies.
7. Amyloidosis:
For cardiac amyloidosis, PET CT can help in:
- Diagnosing and differentiating between different types of amyloidosis.
- Assessing the extent of cardiac involvement.
8. Congenital Heart Disease:
PET CT can assist in the detailed anatomical and functional assessment of congenital heart disease, aiding in:
- Surgical planning.
- Post-operative evaluation.
Advantages of PET CT in Cardiology:
- High Sensitivity and Specificity: PET CT provides high accuracy in detecting and characterizing cardiovascular diseases.
- Quantitative Analysis: PET CT allows for quantitative measurement of myocardial blood flow and metabolism.
- Non-Invasive: It offers a non-invasive alternative to some invasive procedures like coronary angiography.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Combines anatomical and functional imaging in a single session, providing a holistic view of the heart.
Limitations:
- Radiation Exposure: PET CT involves exposure to ionizing radiation, which may limit its use, especially in younger patients or those requiring multiple follow-ups.
- Availability and Cost: PET CT is expensive and not as widely available as other imaging modalities like echocardiography or SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography).
PET CT plays a crucial role in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of various heart diseases. Its ability to provide detailed information on myocardial perfusion, viability, and metabolic activity makes it an invaluable tool in cardiology, particularly for complex cases requiring precise and comprehensive evaluation.
