Hepatobiliary Disease
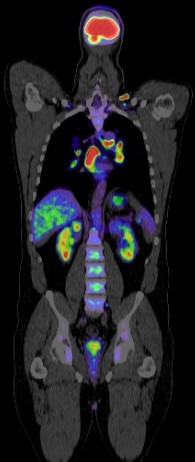

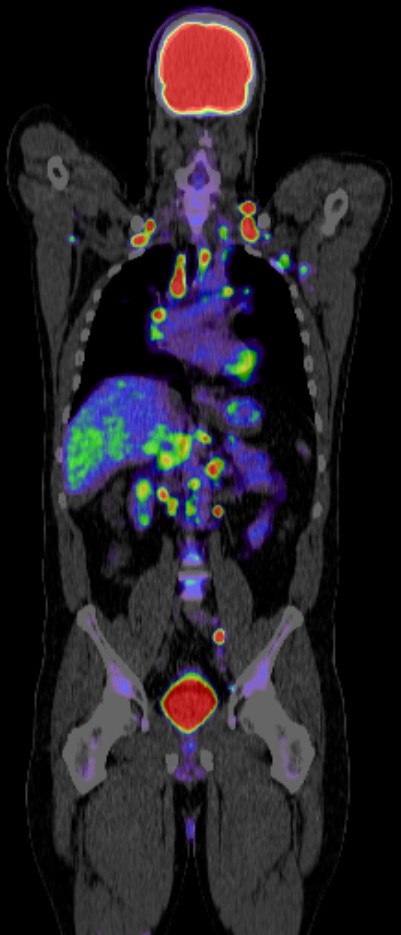
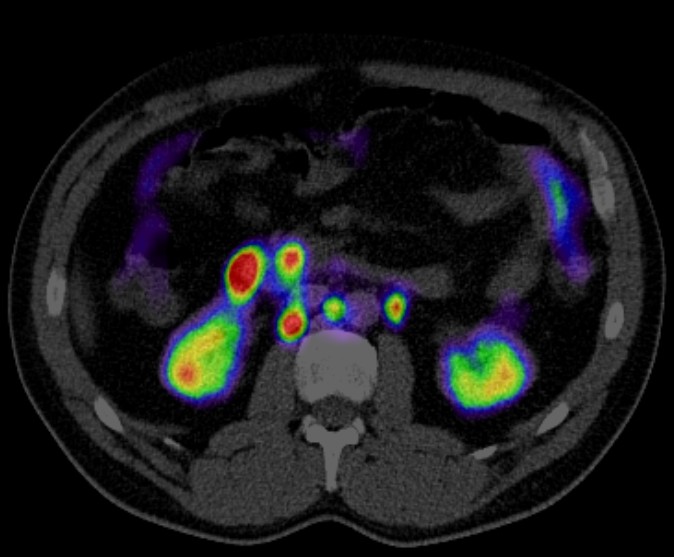
Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography (PET CT) has a significant role in the evaluation and management of hepatobiliary diseases, which include conditions affecting the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and pancreas. Here are some key aspects of its role:
1. Diagnosis and Detection
- Liver Tumors: PET CT is valuable in differentiating benign from malignant liver lesions. Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET CT is particularly useful in detecting primary liver cancers such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer).
- Metastases: It is effective in identifying liver metastases from other primary cancers (e.g., colorectal cancer).
2. Staging
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): PET CT helps in staging HCC by identifying extrahepatic spread, which is crucial for treatment planning.
- Cholangiocarcinoma: It assists in staging by revealing regional lymph node involvement and distant metastases.
3. Assessment of Treatment Response
- Therapy Monitoring: PET CT is used to evaluate the response to treatments such as chemotherapy, radiofrequency ablation, and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). A decrease in FDG uptake after therapy often correlates with a positive treatment response.
- Surgical Planning: Helps in determining the resectability of tumors by assessing the extent of the disease.
4. Recurrence Detection
- Surveillance: PET CT is useful in detecting recurrent disease in patients with a history of hepatobiliary cancers, often before it becomes apparent on conventional imaging techniques.
5. Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Lesions
- Inflammatory vs. Neoplastic: PET CT can help distinguish between inflammatory conditions (like abscesses or benign biliary diseases) and malignancies due to the different metabolic activities of these tissues.
6. Evaluation of Biliary Tract Diseases
- Gallbladder Cancer: PET CT is used to evaluate the extent of gallbladder cancer and its metastasis.
- Bile Duct Obstruction: It can help identify the cause of bile duct obstruction, differentiating between malignant and benign causes.
7. Pancreatic Involvement
- Pancreatic Cancer: PET CT is useful in detecting and staging pancreatic cancer, assessing its relationship with the biliary tract, and evaluating metastatic spread.
Advantages of PET CT
- High Sensitivity and Specificity: PET CT combines the metabolic imaging of PET with the anatomical detail of CT, offering high sensitivity and specificity for many hepatobiliary diseases.
- Whole-Body Imaging: Allows comprehensive staging and detection of distant metastases.
Limitations
- False Positives/Negatives: Inflammatory and infectious processes can sometimes lead to false-positive results. Conversely, some tumors with low metabolic activity might not be detected on FDG PET CT.
- Cost and Accessibility: PET CT is expensive and not universally available, which can limit its use.
PET CT is a powerful tool in the diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatobiliary diseases, significantly impacting clinical decision-making and patient outcomes. Its ability to provide both metabolic and anatomical information makes it superior to many other imaging modalities in specific scenarios.
