Lymphoma
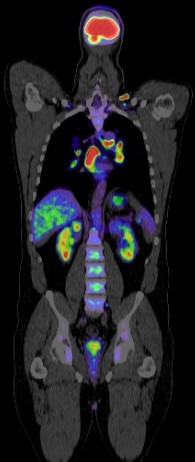

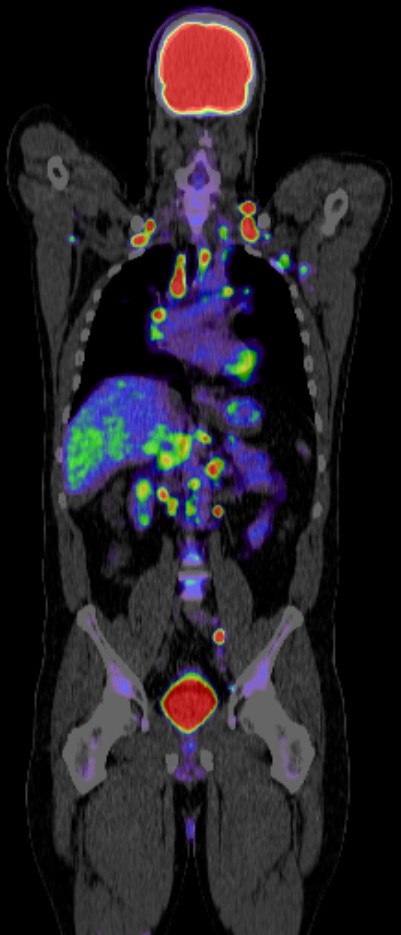
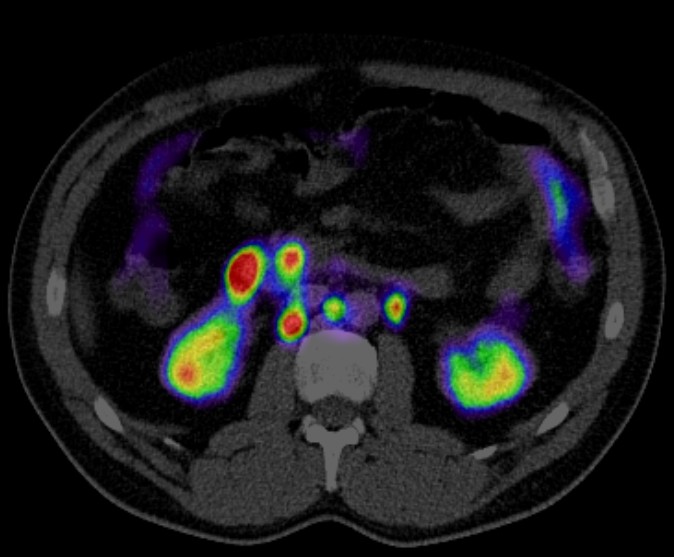
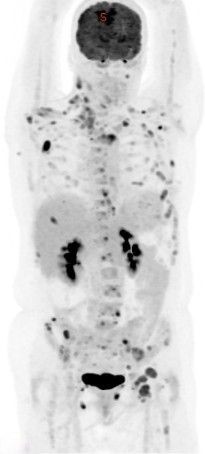
Positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET CT) plays a crucial role in the management of lymphoma, particularly in staging, restaging, treatment response assessment, and surveillance. Here’s how PET CT is used in lymphoma:
Staging: PET CT is highly sensitive in detecting both nodal and extranodal disease involvement. It helps in determining the extent of disease spread, which is crucial for deciding the appropriate treatment strategy. PET CT can identify both primary and metastatic sites of lymphoma involvement.
Treatment Response Assessment: PET CT is used to assess the response to therapy after treatment initiation. It helps differentiate between residual viable tumor tissue and scar tissue or inflammation. A complete metabolic response on PET CT after treatment is associated with better outcomes.
Restaging: PET CT is often performed after completion of treatment to evaluate for residual disease and to confirm complete remission. This is particularly important in lymphoma, where early detection of disease recurrence allows for timely intervention.
Surveillance: After achieving complete remission, patients may undergo periodic PET CT scans to monitor for disease recurrence. Regular surveillance with PET CT helps in early detection of relapse, which can lead to prompt salvage therapy.
Guiding Biopsy: PET CT can guide biopsy by identifying the most metabolically active sites for sampling. This can help ensure accurate diagnosis and staging of lymphoma.
Prognostication: PET CT findings, such as the intensity of metabolic activity (standardized uptake value, SUV), can provide prognostic information. Higher baseline SUV values are associated with poorer prognosis in lymphoma patients.
Overall, PET CT is an invaluable tool in the management of lymphoma, aiding in initial staging, treatment response assessment, restaging, surveillance, biopsy guidance, and prognostication. Its ability to detect metabolic activity complements anatomical imaging provided by CT, leading to improved accuracy in disease detection and management.
