Oesophageal Cancer
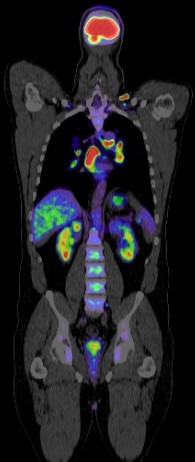

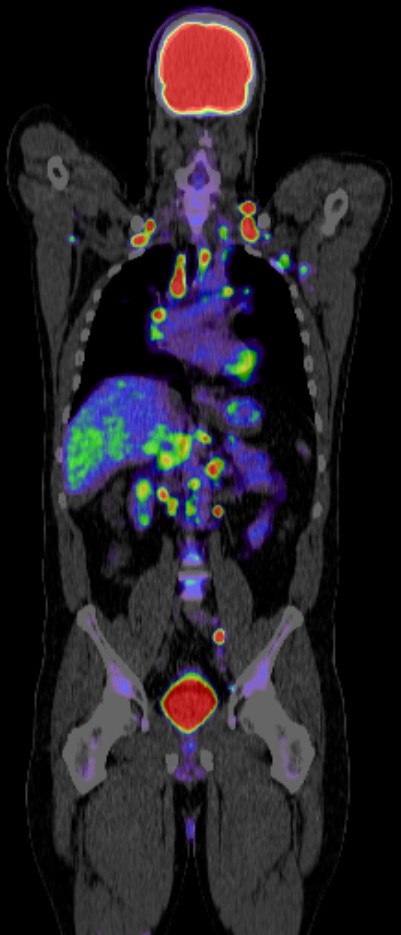
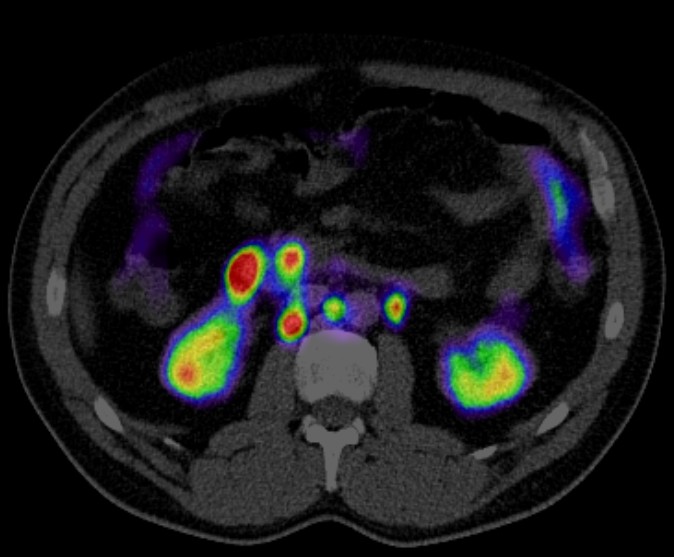
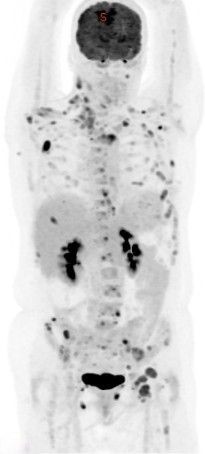
PET CT (Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography) plays a crucial role in the management of esophageal cancer. Here are some key aspects of its role:
Staging: PET CT is valuable for staging esophageal cancer. It helps in determining the extent of the disease, including the primary tumor site, lymph node involvement, and distant metastases. This information is crucial for treatment planning and prognosis estimation.
Treatment Planning: PET CT results influence treatment decisions. It helps in deciding whether surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of these modalities is most appropriate. For instance, if PET CT detects distant metastases, curative surgery might not be recommended, and the focus may shift towards palliative treatment.
Assessment of Treatment Response: After initiating treatment, PET CT is used to evaluate the response to therapy. It helps in assessing tumor regression, detecting residual disease, or identifying disease progression. This information guides further treatment modifications or decisions regarding surgery.
Follow-Up: PET CT is useful in post-treatment surveillance. Regular imaging with PET CT helps in monitoring for disease recurrence or metastases, allowing for timely intervention if necessary.
Prognostic Information: PET CT findings provide valuable prognostic information. Higher metabolic activity on PET CT scans is associated with poorer outcomes, helping in risk stratification and guiding treatment intensity.
Overall, PET CT is an essential tool in the management of esophageal cancer, aiding in staging, treatment planning, response assessment, and follow-up care. However, it is often used in conjunction with other imaging modalities and clinical assessments to provide comprehensive patient care.
