Prostate Cancer
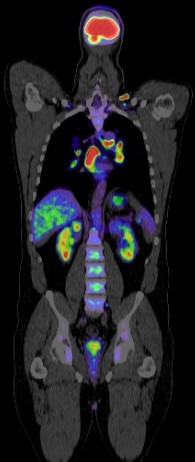

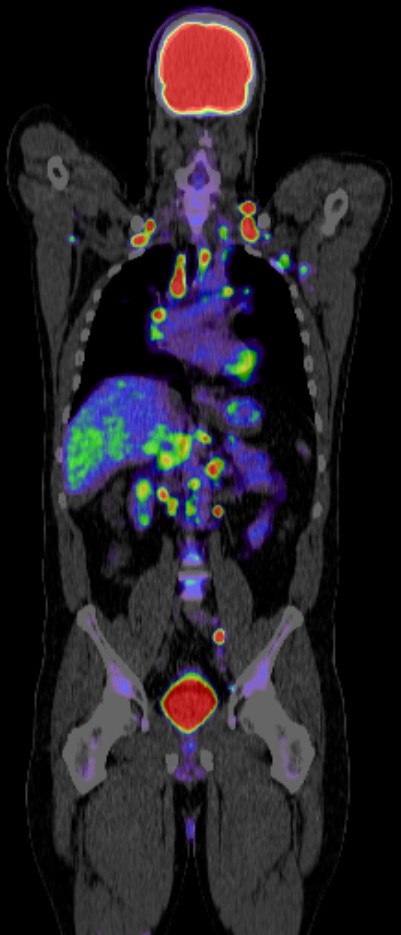
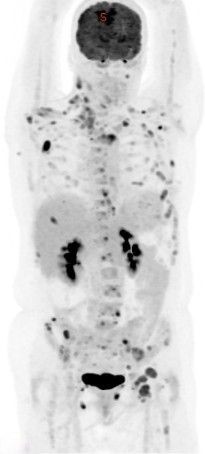
Positron Emission Tomography–Computed Tomography (PET CT) plays a significant role in the management of prostate cancer. Here’s how:
Staging: PET CT helps in accurately staging prostate cancer, determining the extent of the disease spread beyond the prostate gland. It can detect metastases to lymph nodes, bones, and other distant organs, aiding in treatment planning and prognosis estimation. Currently many centres recommend PET CT Scan using the prostate specific radiotracer PSMA to assess patients with high risk prostate cancer, namely a PSA greater than 20ng/ml, stage T3 (spreading outside the prostate capsule, as seen on MRI) or Gleason scores of 8 or more.
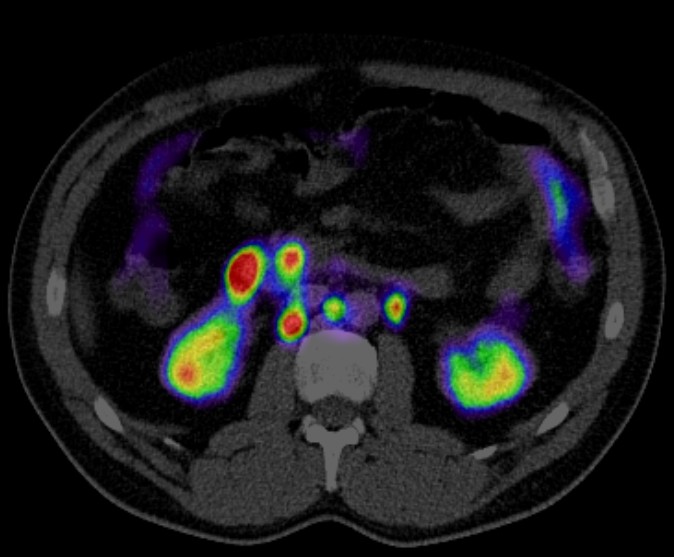
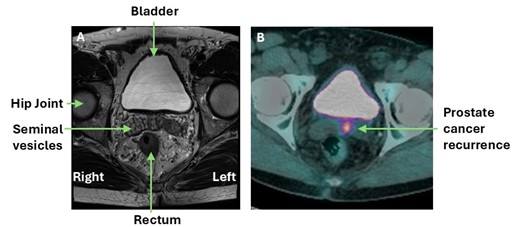
Biochemical Recurrence Detection: After initial treatment, some patients experience a rise in prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, indicating biochemical recurrence. PET CT with specific radiotracers like 18F-PSMA (Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen) and 68Ga-PSMA can localize recurrent disease, guiding salvage therapy decisions such as salvage radiation therapy or salvage prostatectomy. In the image below there is evidence of recurrent prostate cancer in the left seminal vesicle of a patient previously treated disease with external beam radiotherapy. PSMA PET CT scan clearly shows the isolated cancer recurrence which was equivocal on MRI scan. The patient went on to have his seminal vesicle successfully removed by robotic surgery.
Treatment Response Assessment: PET CT can assess treatment response in advanced prostate cancer. It helps evaluate the effectiveness of systemic therapies such as androgen deprivation therapy, chemotherapy, or newer targeted agents. Changes in PET CT findings over time can guide treatment modifications.
Theranostics: PET CT is pivotal in theranostics, a personalized medicine approach that combines diagnostics and therapy. Radiotracers like 177Lu-PSMA are used for both imaging (diagnostics) and targeted radiotherapy (therapy). This approach allows for tailored treatment based on individual tumor characteristics, potentially improving outcomes.
Clinical Trials: PET CT imaging techniques are increasingly incorporated into clinical trials for prostate cancer. They help assess novel imaging agents, therapeutic interventions, and treatment response criteria, contributing to advancements in management.
Overall, PET CT has revolutionized the management of prostate cancer by providing accurate staging, detecting biochemical recurrence, assessing treatment response, enabling theranostics, and facilitating clinical research. Its integration into clinical practice has led to more personalized and effective approaches to prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment
