Stomach Cancer
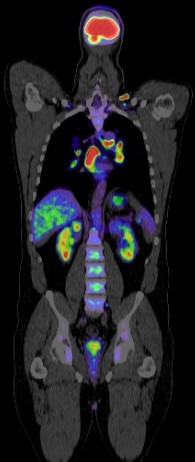

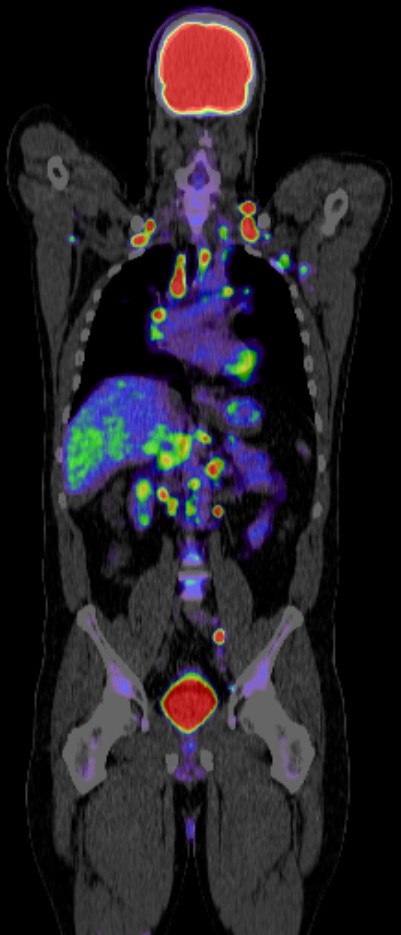
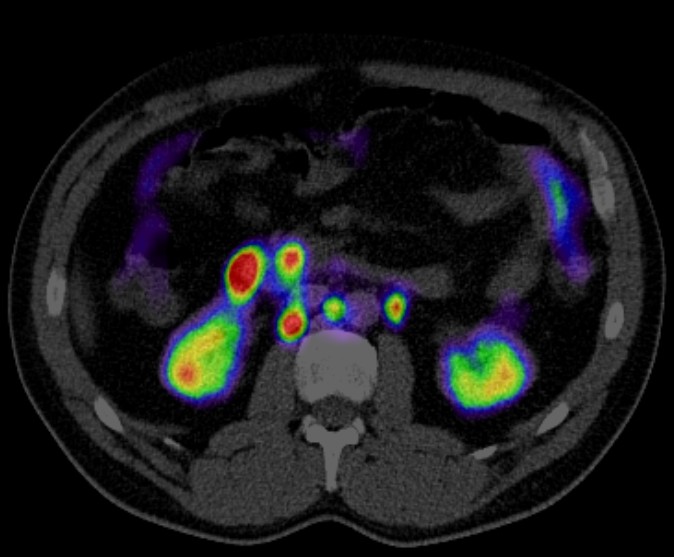
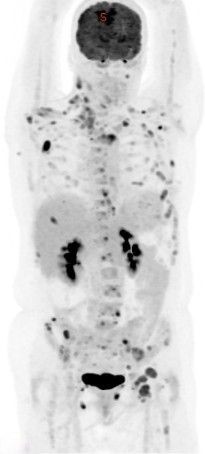
Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography (PET CT) plays a crucial role in the management of stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer. Here’s how PET CT is utilized:
Diagnosis and Staging: PET CT can help in diagnosing stomach cancer by detecting abnormal metabolic activity indicative of cancerous growths. It’s also valuable in staging the disease, determining the extent of cancer spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant organs. This staging information is essential for treatment planning and prognosis assessment.
Treatment Planning: PET CT results help oncologists tailor treatment strategies. For instance, if the cancer has spread beyond the stomach, the treatment plan may include systemic therapies like chemotherapy or targeted therapy, in addition to surgery or radiation therapy.
Monitoring Response to Treatment: After initiating treatment, PET CT scans can be used to monitor how well the treatment is working. Changes in metabolic activity observed on follow-up scans can indicate whether the treatment is effective or if adjustments are necessary.
Detection of Recurrence: PET CT scans are also valuable in detecting cancer recurrence. Even after successful treatment, there’s a risk of cancer returning. PET CT can detect early signs of recurrence by identifying areas of abnormal metabolic activity, prompting further investigation or intervention.
Guiding Surgery: In some cases, PET CT can assist surgeons in planning the surgical approach by providing precise information about the location and extent of the tumor.
Overall, PET CT imaging significantly contributes to the comprehensive management of stomach cancer by aiding in diagnosis, staging, treatment planning, monitoring treatment response, detecting recurrence, and guiding therapeutic interventions.
