Tumour of Unknown Origin
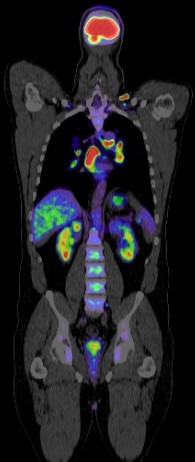

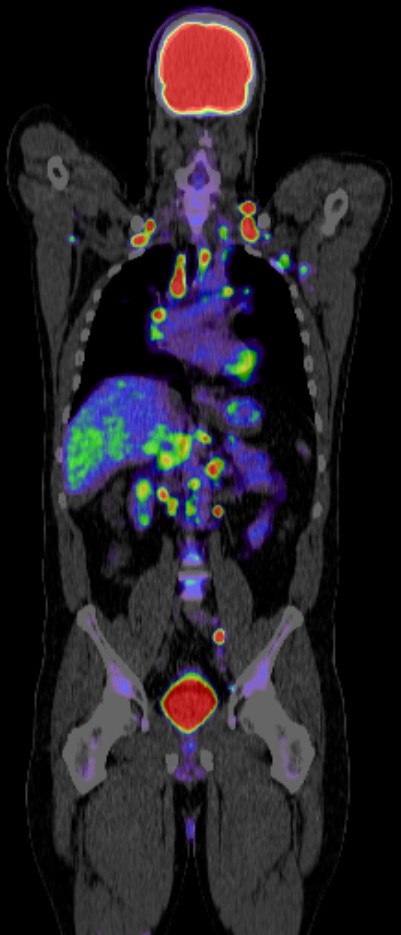
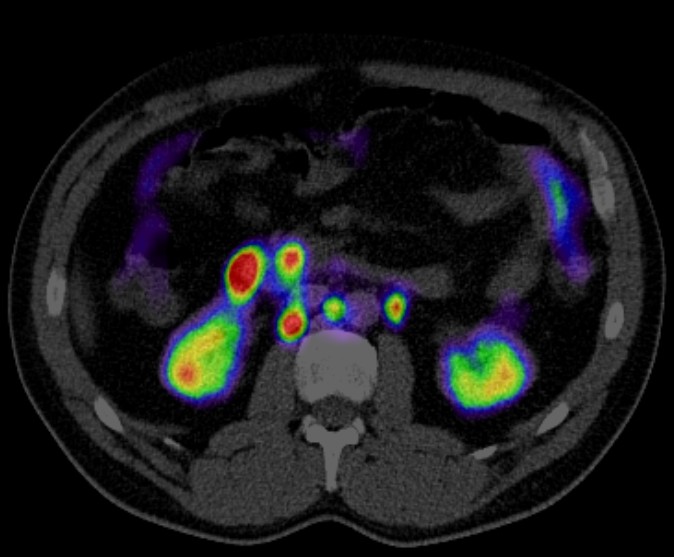
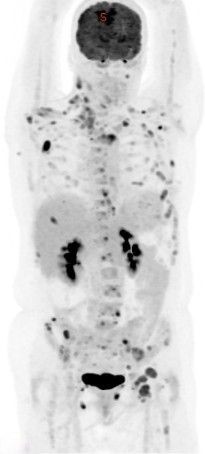
PET CT (Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography) plays a crucial role in the evaluation of tumors of unknown origin (TUO). Here’s how:
Localization: PET CT can help localize the site of the primary tumor in patients presenting with metastatic disease of unknown primary origin. It provides whole-body imaging with high sensitivity, allowing detection of primary tumors even when they are small or in unusual locations.
Characterization: PET CT can help differentiate benign from malignant lesions based on metabolic activity. Malignant tumors often exhibit increased glucose metabolism, which can be visualized on PET CT scans. This information aids in distinguishing between metastatic lesions and benign abnormalities.
Staging: PET CT is valuable for staging the extent of disease in patients with tumors of unknown origin. It helps identify the presence and location of metastases, guiding treatment decisions and prognosis estimation.
Treatment Planning: PET CT findings can influence treatment planning by identifying areas of active disease that may require targeted therapy or radiation. Additionally, PET CT can help monitor response to treatment and detect disease recurrence earlier than conventional imaging modalities.
Biopsy Guidance: In cases where a suspicious lesion is identified on PET CT, it can guide biopsy to obtain tissue for histopathological analysis, aiding in definitive diagnosis and subsequent management.
Prognostication: PET CT findings, particularly the extent of metabolic activity, can provide valuable prognostic information. Higher metabolic activity often correlates with more aggressive disease and poorer prognosis.
Overall, PET CT is a powerful imaging modality in the evaluation of tumors of unknown origin, providing comprehensive information for diagnosis, staging, treatment planning, and prognostication.
